Bitcoins block size
Contents:
We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification. I Accept Show Purposes.
- transfer btc from coinbase to ledger nano s?
- bitcoin mining core i5.
- bitcoin wallet with debit card;
- transfert football bitcoin.
- Conclusion.
- The Block Size Debate: 5 Years Later - Maximillian Laumeister.
- Bitcoin scalability problem - Wikipedia.
Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses.
Blockchain
Part Of. Bitcoin Basics. Bitcoin Mining. How to Store Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Exchanges. Bitcoin Advantages and Disadvantages. Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin Value and Price.
Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain size as of March 27, 2021
Cryptocurrency Bitcoin. Key Takeaways Bitcoin is limited by transaction processing time, an issue that has caused rifts between factions within the bitcoin mining and developing communities. Bitcoin Cash was started by bitcoin miners and developers concerned about the future of the bitcoin cryptocurrency, and its ability to scale effectively. Article Sources. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts.
We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy. Compare Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
Related Articles. Bitcoin Bitcoin vs. Litecoin: What's the Difference? Partner Links.
SegWit Segregated Witness SegWit is the process by which blocks on a blockchain are made smaller by removing signature data from Bitcoin transactions. Category : events. Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in. Namespaces Page Discussion. Views Read View source View history. Sister projects Essays Source. This page was last edited on 24 April , at Content is available under Creative Commons Attribution 3. Privacy policy About Bitcoin Wiki Disclaimers. Yes: "We believe an immediate 2mb blocksize increase is important and urgently required to enable Bitcoin to flourish and deliver more utilitarian use to more people all across the world.
Yes: "We support the Bitcoin Classic proposal [11]. No: "We do NOT support the blocksize increase" [13]. No "At this time, I oppose increasing the block size limit as per Gavin's proposal" - Nadav Ivgi founder [14]. No: "In our mind increasing the block size like this is just pushing the problem a little further at potentially unfixable costs. No [16]. No: "[allow] a sane transaction fee market to emerge, by letting the blocks actually fill-up. Neutral: "We do support bigger blocks and sooner rather than later.
Get the Latest from CoinDesk
But we cannot handle 20 MB blocks right now. I think we can accept 5MB block at most. Yes: "BitcoinReminder. Large institutions will likely continue to favor BTC as the transactions costs are negligible, whereas the minnows will put money into BCH and whatever coin doesn't "mining-fee-to-death" their balance. So THEN the question becomes, who's bigger?
In the end, crypto currencies which can climb high without high mining fees, will win. Which ones are those? Knock, Knock Who's there? Bitcoin Cash Informative and also the style of writing is simply awesome, it seems like you reading a story. Thanks for commenting on my comment, it led me to your blog to find this fantastic article. All posts. Steemit Feedback. Amaze Creater Union. Steem Venezuela. Explore communities…. A brief history of the Bitcoin block size war. Here is a brief history of the attempts on getting the block size limit increased: Early history In Satoshi introduced a 1 MB block size limit.
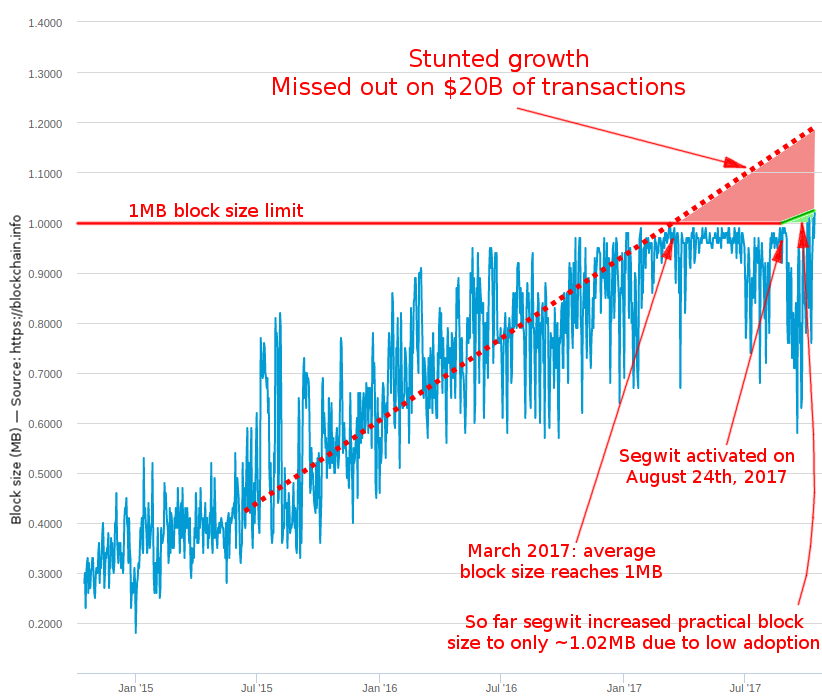
Bitcoin's blocks contain the transactions on the bitcoin network. The on-chain transaction processing capacity of the bitcoin network is limited by the average block creation time of 10 minutes and the block size limit of 1. Perhaps more importantly, it also represented an effective block size limit increase: Bitcoin blocks now have a theoretical maximum size of 4.
The biggest blocks at that time was some few kilobytes big. There exists no official documentation on why the limit was introduced, no comments in the code explaining the rationale, and this limit was committed together with a batch of other changes. Gavin Andresen has explained it was to prevent miners from performing a DoS-attack and only meant to be a temporary measure. During the recent years, people like Gregory Maxwell has suggested it was meant to be a permanent limit preventing the blockchain from becoming too big.
Jeff Garzik proposed to lift the limit already in , claiming the low limit was a "marketing issue". Theymos correctly identified the risk of a chain fork as non-upgraded software would still reject big blocks. Satoshi wrote that the time wasn't ripe for an increase, but that it could be done by hard coding the change to apply from some future in his example, timestamp or block height, giving people sufficient time to upgrade.
During there was much discussions; some people where annoyed having to carry the cost of storing gigabytes of gambling spam forever. The concepts of "soft fork" and "hard fork" was introduced. See also my forks for dummies article The notion "hard forks are inherently unsafe and we need absolutely full consensus to implement that" came into existence.